Writing to a TMP102 Temperature Sensor Using I2C
This example demonstrates how to read from and write to a TMP102 temperature sensor using the I2C protocol.
The full discussion can be found in the Wilderness Labs Developer portal.
Hardware
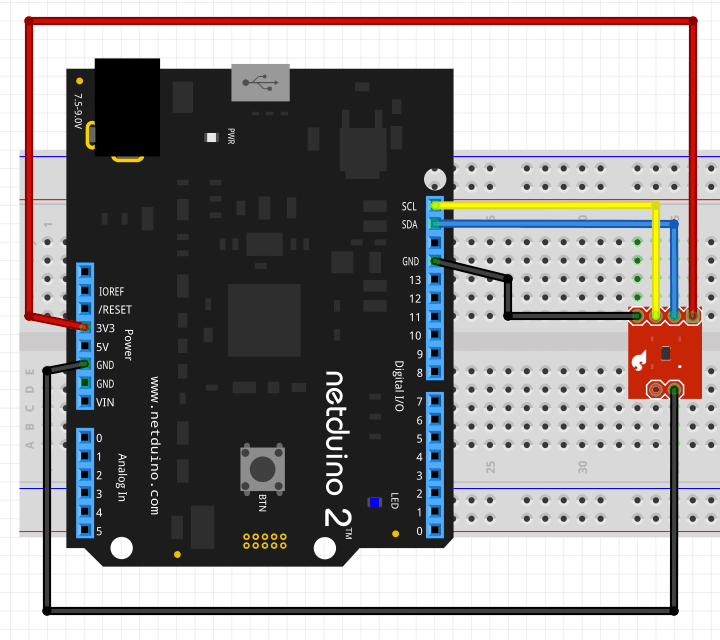
Code
using Microsoft.SPOT;
using Microsoft.SPOT.Hardware;
using System.Threading;
namespace TMP102ReadWrite
{
public class Program
{
/// <summary>
/// Convert a byte to a two character hex string.
/// </summary>
/// <returns>Hexadecimal representation of the byte as a string.</returns>
/// <param name="val">Byte to convert into a string.</param>
public static string ByteToHex(byte val)
{
const string hex = "0123456789abcdef";
return(new string(new char[] { '0', 'x', hex[(val & 0xf0) >> 4], hex[val & 0x0f] }));
}
/// <summary>
/// Reads the TMP 102 configuration.
/// </summary>
/// <remarks>
/// Create transactions to read the current configuration. A write transaction
/// is necessary to change the pointer register to point to the configuration
/// registers. A read transaction will then read the current configuration.
/// </remarks>
/// <param name="device">TMP102 I2CDevice object to read the configuration from.</param>
private static byte[] ReadTMP102Configuration(I2CDevice device)
{
I2CDevice.I2CTransaction[] readConfiguration = new I2CDevice.I2CTransaction[2];
byte[] pointerBuffer = new byte[1];
pointerBuffer[0] = 1;
readConfiguration[0] = I2CDevice.CreateWriteTransaction(pointerBuffer);
//
byte[] currentConfig = new byte[2];
readConfiguration[1] = I2CDevice.CreateReadTransaction(currentConfig);
device.Execute(readConfiguration, 100);
Debug.Print("Configuration register: " + ByteToHex(currentConfig[0]) + ", " + ByteToHex(currentConfig[1]));
return (currentConfig);
}
/// <summary>
/// Main program loop.
/// </summary>
public static void Main()
{
//
// Create a new I2C device for the TMP102 on address 0x48 with the clock
// running at 50 KHz.
//
I2CDevice tmp102 = new I2CDevice(new I2CDevice.Configuration(0x48, 50));
//
// Read the configuration prior to updating the conversion mode to 13-bit mode.
//
byte[] currentConfig = ReadTMP102Configuration(tmp102);
//
// Now we have the configuration, set up to change the configuration between
// 12 and 13 bit mode and read data from the sensor.
//
I2CDevice.I2CTransaction[] changeConfig = new I2CDevice.I2CTransaction[1];
byte[] newConfiguration = { 0x01, currentConfig[0], (byte) (currentConfig[1] | 0x10) };
changeConfig[0] = I2CDevice.CreateWriteTransaction(newConfiguration);
tmp102.Execute(changeConfig, 100);
Thread.Sleep(1000);
//
// Now setup for reading the temperature.
//
I2CDevice.I2CTransaction[] reading = new I2CDevice.I2CTransaction[2];
byte[] repointToTemperatureRegister = { 0x00 };
reading[0] = I2CDevice.CreateWriteTransaction(repointToTemperatureRegister);
byte[] temperatureData = new byte[2];
reading[1] = I2CDevice.CreateReadTransaction(temperatureData);
while (true)
{
//
// Read the temperature.
//
int bytesRead = tmp102.Execute(reading, 100);
Debug.Print("Temperature data: "+ ByteToHex(temperatureData[0]) + ", " + ByteToHex(temperatureData[1]));
//
// Convert the reading into Centigrade and Fahrenheit.
//
int sensorReading = 0;
double centigrade = -273.15;
double fahrenheit = centigrade * 1.8 + 32;
if ((temperatureData[1] & 0x01) == 1)
{
sensorReading = ((temperatureData[0] << 5) | (temperatureData[1]) >> 3);
Debug.Print("13-bit value retrieved.");
}
else
{
sensorReading = ((temperatureData[0] << 4) | (temperatureData[1]) >> 4);
Debug.Print("12-bit value retrieved.");
}
centigrade = sensorReading * 0.0625;
fahrenheit = centigrade * 1.8 + 32;
//
// Display the readings in the debug window and pause before repeating.
//
Debug.Print(centigrade.ToString() + " C / " + fahrenheit.ToString() + " F");
Thread.Sleep(1000);
}
}
}
}
Hardware Required
- Netduino
- TMP102 I2C Temperature Sensor
Netduino Samples Github Repository
Full source code for all of the samples can be found in the Netduino Samples repository on Github.