N-Channel Low-Side
Low-Side vs. High-Side
When using transistors, they are place on either the HIGH side or the LOW side of the load they're controlling. If the switch is on side that is closer to the higher voltage, it's said to be on the HIGH side, and if it's closer to the lower voltage (typically GND), then it's on the LOW side:
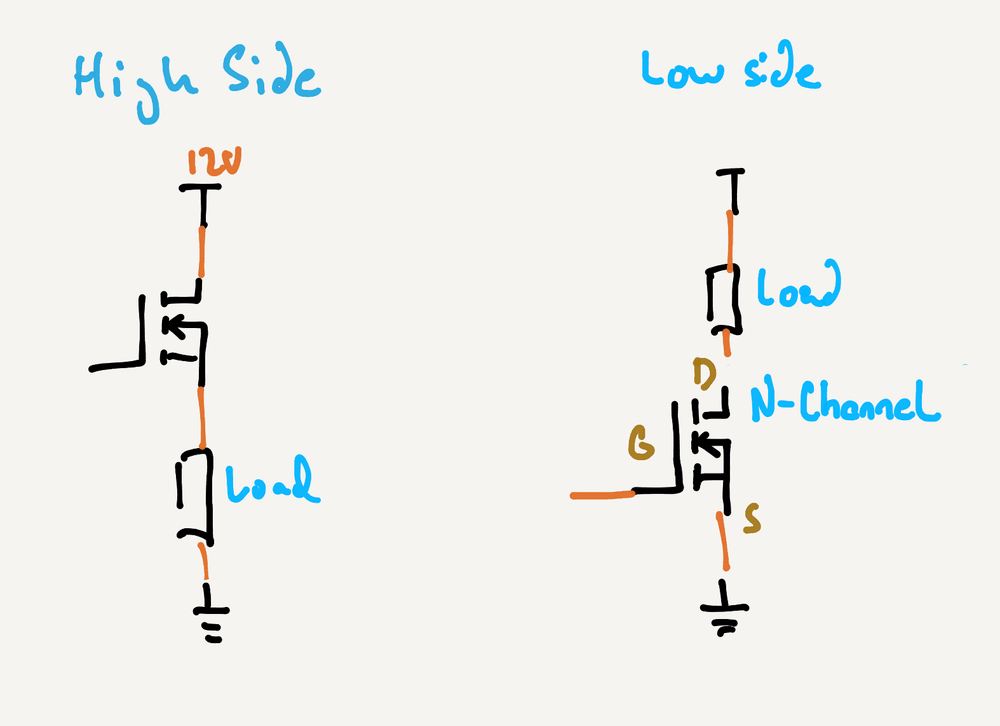
[NOTE - genericize the MOSFET symbol to a switch so we don't complicate. Also get rid of 12V and put like +V]
Using an N-Channel MOSFET as a Low-Side Switch
Let's say we wanted to control a load such as a DC motor. A very simple and efficient design would be via a low-side, N-Channel MOSFET:

In this case, the voltage between the Gate and Source is +3.3V. It enables the Gate to fill with positively charged holes, which attract the minority charge carriers from the surrounding P-Channel semiconductor, in this case, the negatively charged electrons to create an N-Channel conductor between Drain and Source:
High-side switching isn't always possible, however. Sometimes we need to use a switch on the high side to provide a component or a circuit with a HIGH signal.
